Usando las GPO’s de VMware View 4.6
En este documento veremos las directivas que podremos aplicar a nivel de Directorio Activo a nuestro entorno VMware View, ya que disponemos de diversas plantillas administrativas para poder gestionar los agentes, clientes, servidores, configuración común y sobre todo si necesitamos optimizar el protocolo PCoIP. En el documento se muestran todas las GPO’s existentes para poder gestionar de una forma centralizada nuestro VMware View 4.6, eso sí en inglés 😉
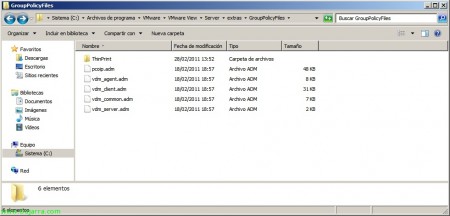
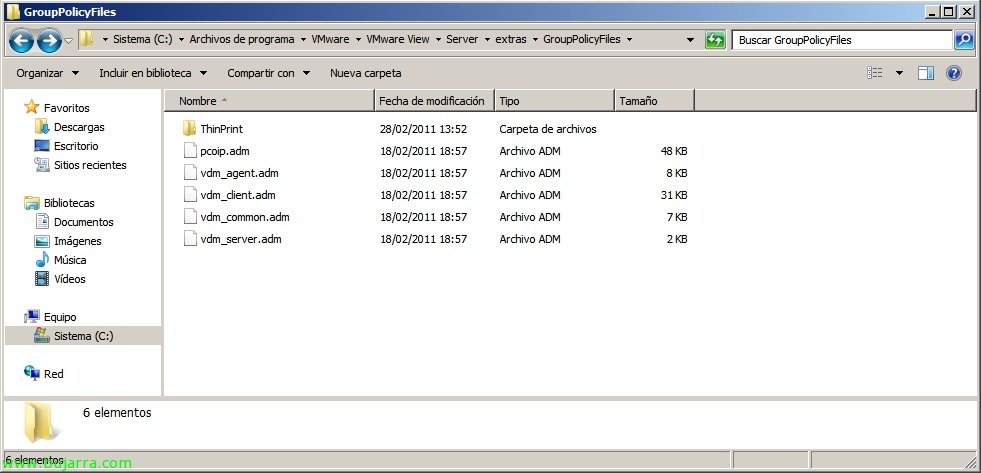
Podremos encontrar las plantillas de las directivas en cualquier servidor Connection Server en %ProgramFiles%VMwareVMware ViewServerextrasGroupPolicyFiles, estas las importaremos en GPO’s nuevas que generemos desde nuestros controladores de dominio.
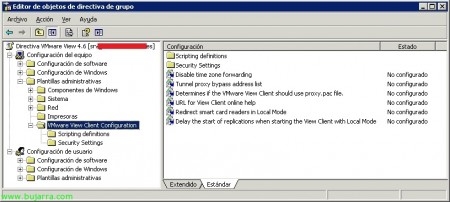
GPO de VMware View Client,
En “Configuración de equipo” > “Plantillas administrativas” > “VMware View Client Configuration”:
Disable time zone forwarding
Determines if the time zone of the View desktop is synchronized with that of the connected client. When enabled, this property will only apply if the Disable Time Zone Synchronization property of the View Agent Configuration policy is not set to disabled.
This property is disabled by default.
Tunnel proxy bypass address list
Do not use proxy server for tunnel addresses beginning with specified string, use semicolon (;) to separate entries.
Determines if the VMware View Client should use proxy.pac file.
Determines if the VMware View Client should use proxy.pac file.
URL for View Client online help
Specifies an alternate URL from which View Client can retrieve help pages. This property is intended for use in environments that do not possess Internet access and can therefore not retrieve the remotely-hosted help system.
Redirect smart card readers in Local Mode
Determines if smart card readers are automatically redirected to Local Mode desktops. The readers will be shared with the client machine. This setting is enabled by default.
Delay the start of replications when starting the View Client with Local Mode
Delay all replications by this many seconds after the View Client with Local Mode is started. Replications will continue on their normal schedule after this delay. The default delay is 900 seconds (15 minutes).
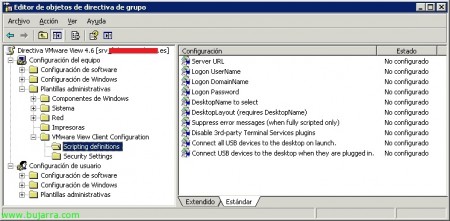
En “Configuración de equipo” > “Plantillas administrativas” > “VMware View Client Configuration” > “Scripting definitions”:
Server URL
Determines the URL used by View Client during login. For example: http://view1.example.com
Logon UserName
Determines the username used by View Client during login.
Logon DomainName
Determines the NETBIOS domain used by View Client during login. For example: EXAMPLE
Logon Password
Determines the password used by View Client during login.
Warning: this password is stored in plain text by Active Directory
DesktopName to select
Determines the default desktop used by View Client during login.
DesktopLayout (requires DesktopName)
Determines the display state of the View Client window when the desktop is launched.
Note: This property is only available when the ‘DesktopName to select’ property has been set.
Disable 3rd-party Terminal Services plugins
Determines if error messages are displayed during login.
Note: This property is only applied when the login process is fully scripted, that is, when all the requisite login information has been pre-populated beforehand through policy.
Note: If the login fails on account of incorrect login information being entered, the user is not notified and the View Client wswc.exe process will continue to run in the background.
Connect all USB devices to the desktop on launch
Automatically connects all available USB devices on the host to a desktop when that desktop is launched.
Connect USB devices to the desktop when they are plugged in
Automatically connects USB devices when they are plugged in to the host to the desktop with which the user is currently working.
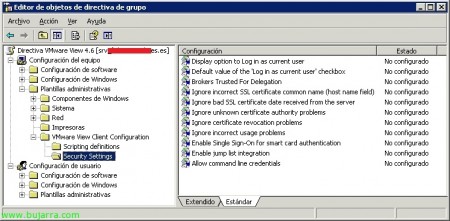
En “Configuración de equipo” > “Plantillas administrativas” > “VMware View Client Configuration” > “Security Settings”:
Display option to Log in as current user
Determines if the Log in as current user checkbox is visible in the Windows View Client.
This setting is enabled by default.
If this option is set to ‘off’, the user will not be able to override the ‘Default value of Log in as current user checkbox’ option.+
Default value of the ‘Log in as current user’ checkbox
Sets whether the ‘Log in as current user’ checkbox is checked by default.
This setting is disabled by default.
Brokers Trusted For Delegation
Sets the list of brokers that are allowed to have credentials delegated to them. This is used with ‘Log in as current user’.
By default all brokers are trusted
You can add brokers using any of 3 different formats:
domainsystem$
system$@domain.dom
SPN (Service Principal Name)
Ignore incorrect SSL certificate common name (host name field)
Determines if errors associated with incorrect server certificate common names are disabled.
This error occurs when the common name on the certificate does not correlate with the hostname of the server that sends it.
Ignore bad SSL certificate date received from the server
Determines if errors associated with invalid server certificate dates are disabled.
This error occurs when the date on certificate sent by the server has passed.
Ignore unknown certificate authority problems
Determines if errors associated with an unknown certification authority on the server certificate are ignored.
This error occurs when the certificate sent by the server is signed by an untrusted third-party authority.
Ignore certificate revocation problems
Determines if errors associated with a revoked server certificate are ignored.
These errors occur when the certificate sent by the server has been revoked or the client cannot verify the certificate’s revocation status.
This setting is disabled by default.
Ignore incorrect usage problems
Determines if errors associated with incorrect usage of a server certificate are ignored.
This error occurs when the certificate sent by the server intended for some purpose other than verifying the identity of the sender and encrypting server communications.
Enable Single Sign-On for smart card authentication
Enables Single Sign-On for smart card authentication. This requires the View Client to store the encrypted smart card PIN in memory momentarily before submitting it to the View Connection Server.
Enable jump list integration
Enables adding a jump list to the View Client icon in the taskbar on Windows 7 and later to allow users to easily connect to recent View Connection Servers and remote desktops. This feature is enabled by default.
Allow command line credentials
Allow credentials such as a password or PIN to be provided via command line parameters.
This setting is enabled by default.
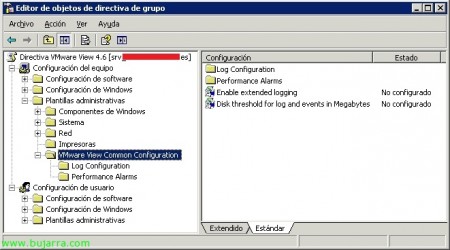
GPO de configuración común de VMware View,
En “Configuración de equipo” > “Plantillas administrativas” > “VMware View Common Configuration”:
Enable extended loging
Determines if trace and debug events are included in the log files
Disk threshold for log and events in Megabytes
Specifies the minimum remaining disk space threshold for logs and events. If no value is specified, a default of 200 applies. When this value is reached, event logging will stop.
En “Configuración de equipo” > “Plantillas administrativas” > “VMware View Common Configuration” > “Log Configuration”:
Number of days to keep production logs
Specifies the number of days for which log files are retained on the system. If no value is set, the default applies and log files will only be kept for 7 days.
Maximum number of debug logs
Specifies the maximum number of debug log files to retain on the system. When a log file reaches its maximum size, no further entries are added and a new log file is created. When the number of previous log files reaches this value, the oldest log file is deleted.
Maximum debud log size in Megabytes
Specifies the maximum size in Megabytes that a debug log can reach before the log file is closed and a new log file is created.
Log directory
The full path to the directory for log files. If this location is not writable, the default location is used. Note that for client log files, an extra directory with the client name is created for the logs.
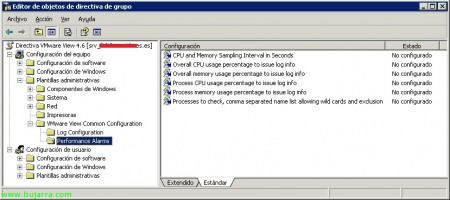
En “Configuración de equipo” > “Plantillas administrativas” > “VMware View Common Configuration” > “Performance Alarms”:
CPU and Memory Sampling Interval in Seconds
Specifies the interval at which the CPU and memory are polled. Please note that a low sampling interval may result in an extremely high level of output being written to the log.
Overall CPU usage percentage to issue log info
The threshold at which the overall CPU use of the system is logged. Note that where multiple processors are available, this percentage represents the combined usage.
Overall memory usage percentage to issue log info
The threshold at which the overall committed system memory use (memory that has been allocated by processes and to which the operating system has committed physical memory and/or a page slot in the pagefile) is logged.
Process CPU usage percentage to issue log info
The threshold at which the CPU usage of any individual process is logged.
Process memory usage percentage to issue log info
The threshold at which the memory usage of any individual process is logged.
Processes to check, comma separated name list allowing wild card and exclusion
A comma-separated list of queries that correspond to the name of one or more processes to be examined. In order to filter the list, you can use the following wildcards within each query: an asterisk (*) that matches zero or more characters, a question mark (?) that matches exactly one character, and an exclamation mark (!) that can be used as a prefix to a query in order to exclude any results yielded by that query. For example: ‘!*sys,ws*’ – select all processes starting with ‘ws’ but exclude all processes ending with ‘sys’.
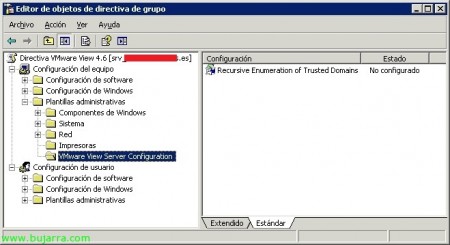
GPO de servidores VMware View,
En “Configuración de equipo” > “Plantillas administrativas” > “VMware View Server Configuration”:
Recursive Enumeration of Trusted Domains
Determines if every domain trusted by the domain in which the server resides is enumerated. In order to establish a complete chain of trust, the domains trusted by each trusted domain are also enumerated and the process continues recursively until all trusted domains are discovered. This information is passed to View Connection Server in order to ensure that all trusted domains are available to the client on login.
This property is enabled by default. When disabled, only directly trusted domains are enumerated and connection to remote domain controllers does not take place.
Note: In environments with complex domain relationships — such as those that use multiple forest structures with trust between domains in their forests — this process can take a few minutes to complete.
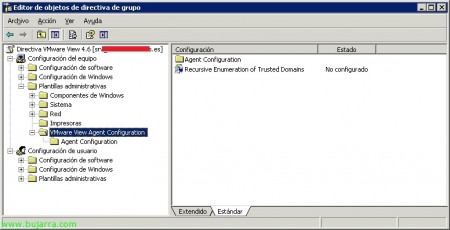
GPO del agente de VMware View,
En “Configuración de equipo” > “Plantillas administrativas” > “VMware View Agent Configuration”:
Recursive Enumeration of Trusted Domains
Determines if every domain trusted by the domain in which the server resides is enumerated. In order to establish a complete chain of trust, the domains trusted by each trusted domain are also enumerated and the process continues recursively until all trusted domains are discovered. This information is passed to View Connection Server in order to ensure that all trusted domains are available to the client on login.
This property is enabled by default. When disabled, only directly trusted domains are enumerated and connection to remote domain controllers does not take place.
Note: In environments with complex domain relationships — such as those that use multiple forest structures with trust between domains in their forests — this process can take a few minutes to complete.
En “Configuración de equipo” > “Plantillas administrativas” > “VMware View Agent Configuration” > “Agent Configuration”:
Force MMR to use software overlay
MMR will try to use the hardware overlay to play back video for better performance. However, when working with multiple displays the hardware overlay will only exist on one of the displays: either the primary display or the display where WMP was started. If WMP is dragged to another display the video is shown as a black rectangle. Use this option to force MMR to use a software overlay which will work on all displays.
AllowDirectRDP
Determines if non-View clients can connect directly to View desktops using RDP. When disabled, the agent will only permit View-managed connections via View Client or View Portal.
This property is enabled by default.
AllowSingleSignOn
Determines if single sign-on (SSO) is used to connect users to View desktops. When enabled, users are only required to enter their credentials when connecting with View Client or View Portal. When disabled, users must reauthenticate when the remote connection is made.
This property requires that the Secure Authentication component of View Agent is installed on the desktop, and is enabled by default.
ConnectionTicketTimeout
Specifies the time in seconds for which the View connection ticket is valid. The connection ticket is used by View clients when connecting to View Agent and is used for verification and single sign-on purposes.
For security reasons, these tickets are only valid within the specified time period. If this property is not explicitly set, a default of 900 seconds applies.
CredentialFilterExceptions
A semi-colon separated list of executable file names that is not allowed to load the agent CredentialFilter. The file names must be without path and suffix.
Connect using DNS Name
Determines if the View Connection Server uses the DNS name of the machine to connect to, rather than its IP address. This is often used in a NAT/Firewall situation when the View Client or View Connection Server cannot use the desktop IP address directly.
This property is disabled by default.
Disable Time Zone Synchronization
Determines if the time zone of the View desktop is synchronized with that of the connected client. When enabled, this property will only apply if the ‘Disable time zone forwarding’ property of the View Client Configuration policy is not set to disabled.
This property is disabled by default.
Toggle Display Settings Control
Determines whether to disable the Settings page of the Display Control Panel applet while a View Client is connected.
This property only applies to sessions using the PCoIP protocol. This property is enabled by default.
CommandsToRunOnConnect
The list of commands to be run when a session is connected for the first time.
CommandsToRunOnReconnect
The list of commands to be run when a session is re-connected after a disconnect.
ShowDiskActivityIcon
Shows a disk activity icon in the system tray. Uses the ‘System Trace NT Kernel Logger’ which can only be used by a single process, disable if needed for other purposes. Default is Enabled.
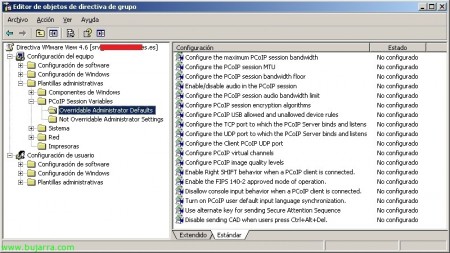
GPO de PCoIP,
En “Configuración de equipo” > “Plantillas administrativas” > “PCoIP Session Variables”:
Configure the maximum PCoIP session bandwidth
This policy constrains the maximum link rate (i.e. the peak bandwidth on the wire) in a PCoIP session. This includes all imaging, audio, virtual channel, USB and control PCoIP traffic.
Set this value to the overall capacity of the link to which your endpoint is connected. E.g. a client connecting through a 4Mbit/s Internet connection should set this value to 4Mbit (or perhaps 10% less) to prevent the server from attempting to transmit at a higher rate which would cause excessive packet loss and a poorer user experience. This value is symmetric, i.e. it forces the client and server down to the lowest of what is set on the client or server side. So in the 4Mbit/s example described above the setting forces the server to transmit at a lower rate even though the parameter is set on the client.
This policy applies to both server and client; the bandwidth is limited to be the minimum of the server and client settings.
Leaving this policy Disabled or Not Configured on an endpoint means that the endpoint imposes no bandwidth constraints, otherwise when Configured the setting is used as the endpoint’s maximum bandwidth constraint in kilobits per second. The default when Configured is 1000000 kbits/second (1 gigabit).
Configure the PCoIP session MTU
This policy can be used to set the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) size for UDP packets for a PCoIP session.
This MTU size includes the IP and UDP packet headers. (TCP uses the standard MTU discovery mechanism to set MTU and is not affected by this setting.) The MTU size will not generally need to be changed from the default unless there is an unusual network setup which causes PCoIP packet fragmentation.
This policy applies to both server and client; the MTU is negotiated to be the minimum of the server and client settings.
Leaving this policy Disabled or Not Configured means that the default will be used by this endpoint in the negotiation otherwise the Configured value will be used by this endpoint in the negotiation. The MTU setting has a maximum value of 1500 and a minimum value of 500. The default MTU setting is 1300 bytes.
Configure the PCoIP session bandwidth floor
This policy sets a lower limit to the bandwidth reserved by the PCoIP session.
This parameter sets a lower bound on the expected bandwidth transmit rate for the endpoint. This parameter can be used to effectively reserve bandwidth for an endpoint. This improves the responsiveness because a user does not need to wait for bandwidth to become available. Note that it is important to ensure that for a given configuration, the sum of all the floors for all connections does not exceed the network capability (over-subscribing).
This policy applies to both server and client but the setting only affects the endpoint on which it is configured.
Leaving this policy Disabled, Not Configured or Configured with a value of 0 means no (reserved) bandwidth constraints, otherwise the value is used as the reserved bandwidth floor in kilobits per second. The default when Configured is 0, i.e. no configured bandwidth reserved.
Enable/disable audio in the PCoIP session
This policy controls whether audio is enabled in PCoIP sessions.
This policy applies to both server and client – the use of Audio is negotiated between the server and client endpoints. Both endpoints must have audio enabled before audio will be used.
When the setting is Disabled or Not Configured, the default (audio enabled) is used for the endpoint in the negotiation. When the setting is Configured and the “Disable audio in PCoIP sessions” checkbox is checked then audio will be disabled regardless of the other endpoint’s setting.
Configure the PCoIP session audio bandwidth limit
This policy constrains the maximum bandwidth that can be used for audio (sound playback) in a PCoIP session.
The audio processing monitors the bandwidth utilized for audio at any given time. The processing selects the audio compression algorithm used based on providing the best audio possible given the current bandwidth utilization. If the bandwidth limit is set then the quality is reduced (by changing the compression algorithm selection) until the bandwidth limit can be respected. If minimum quality audio cannot be provided within the bandwidth limit specified then audio is disabled.
To allow for uncompressed high quality stereo audio the value for this setting should be above 1600 kbit/s. A value setting of 450 kbit/s and higher will allow for stereo high quality compressed audio. A value setting between 50 kbit/s and 450 kbit/s will result in audio ranging between FM radio and phone call quality. A value setting below 50 kbit/s may result in no audio playback.
This policy applies to the server only. Note that Audio must be enabled on both endpoints before this setting has any effect.
Leaving this policy Disabled or Not Configured uses a default audio bandwidth limit of 500 kilobits per second to constrain the audio compression algorithm selected. When Configured the setting value will be used as the audio bandwidth limit in kilobits per second with a default audio bandwidth limit of 500 kilobits per second.
Note that this setting is applicable to View 4.5.1 and later versions; this setting will have no effect on earlier versions.
Configure PCoIP session encryption algorithms
This policy controls the encryption algorithms advertised by the PCoIP endpoint during session negotiation. At least one algorithm must be enabled.
This setting applies to both server and client. The endpoints negotiate the actual session encryption algorithm used. Note that AES-128-GCM encryption is always overridden to enabled if FIPS140-2 approved mode is enabled.
Leaving this policy Disabled or Not Configured leaves both Salsa20-256round12 and AES-128-GCM algorithms available for negotiation by this endpoint. When Configured, checking one of the checkboxes will disable the associated encryption algorithm – note that at least one encryption algorithm must be enabled. The default when Configured leaves both algorithms available for negotiation by this endpoint.
Configure PCoIP USB allowed and unallowed device rules
This policy sets USB device authorizations and unauthorizations for PCoIP sessions using a Teradici Zero Client.
When the policy is enabled, for a USB device to be used in a PCoIP session it must be included on the USB authorization list and not present on the USB unauthorization list.
USB authorizations:
An empty USB authorization string means that no USB devices are authorized. Up to ten USB authorization rules may be defined and each rule can be either a specific Vendor ID (VID) and Product ID (PID) or describe a class of USB devices. Rules are separated by the ‘|’ character.
A VID/PID rule is formatted as 1xxxxyyyy where xxxx is the device’s VID in hexadecimal format and yyyy is the PID in hexadecimal format. The rule to authorize a device with VID=0x1a2b and PID=0x3c4d is ’11a2b3c4d’.
A class rule can allow an entire device class, a single sub-class or a protocol within a sub-class. A class rule uses one of the following forms:
1. Allow all USB devices: ’23XXXXXX’
2. Allow USB device class ID 0xaa: ’22aaXXXX’
3. Allow USB device sub-class 0xbb in device class 0xaa: ’21aabbXX’
4. Allow USB protocol 0xcc in sub-class 0xbb in class 0xaa: ’20aabbcc’
For example, the USB authorization string to allow USB HID (mouse and keyboard) devices (class ID 0x03) and webcams (class ID 0x0e) is ‘2203XXXX|220eXXXX’
USB unauthorizations:
An empty USB unauthorization string means that no USB devices are banned. Up to ten USB unauthorization rules may be defined and each rule can be either a specific Vendor ID (VID) and Product ID (PID) or describe a class of USB devices. Rules are separated by the ‘|’ character.
A VID/PID rule is formatted as 1xxxxyyyy where xxxx is the device’s VID in hexadecimal format and yyyy is the PID in hexadecimal format. The rule to block a device with VID=0x1a2b and PID=0x3c4d is ’11a2b3c4d’.
A class rule can disallow an entire device class, a single sub-class or a protocol within a sub-class. A class rule uses one of the following forms:
1. Disallow USB device class ID 0xaa: ’22aaXXXX’
2. Disallow USB device sub-class 0xbb in device class 0xaa: ’21aabbXX’
3. Disallow USB protocol 0xcc in sub-class 0xbb in class 0xaa: ’20aabbcc’
For example, the USB authorization string to disallow USB Mass Storage devices (class ID 0x08) ‘2208XXXX’
This setting applies only to the server and only when the server is in a session with a Teradici Zero Client. Device usage is negotiated between the endpoints – for a USB device to be used in a PCoIP session it must be included on the USB authorization list and not present on the USB unauthorization list.
When Disabled or Not Configured, all devices are allowed and none are disallowed. When Configured the default is that all devices are allowed and none are disallowed otherwise the authorization and unauthorization strings are interpreted as described above.
Configure the TCP port to which the PCoIP Server binds and listens
This policy sets the TCP server port bound to by software PCoIP hosts.
The TCP port value sets the base TCP port that the server attempts to bind to. The TCP port range value determines how many additional ports should be tried if the base port is not available. The range spans from (base port) to (base port + port range). The port range must be between 0 and 10.
This setting applies to the server only.
When Disabled or Not Configured, the base TCP port is 50002 for versions of View prior to View 4.5 (i.e. View 4.0, 4.0.1 and 4.0.2) and 4172 for View 4.5 and subsequent versions. When Disabled or Not Configured, the port range is 1. When Configured, the base port and port range values are applied as described above with a default base port of 4172 and a default port range of 1.
Configure the UDP port to which the PCoIP Server binds and listens
This policy sets the UDP server port bound to by software PCoIP hosts.
The UDP port value sets the base UDP port that the server attempts to bind to. The UDP port range value determines how many additional ports should be tried if the base port is not available. The range spans from (base port) to (base port + port range). The port range must be between 0 and 10.
This setting applies to the server only.
When Disabled or Not Configured, the base UDP port is 50002 for versions of View prior to View 4.5 (i.e. View 4.0, 4.0.1 and 4.0.2) and 4172 for View 4.5 and subsequent versions. When Disabled or Not Configured, the port range is 10. When Configured, the base port and port range values are applied as described above with a default base port of 4172 and a default port range of 10.
Configure the Client PCoIP UDP port
This policy sets the UDP client port used by software PCoIP clients in attempting to establish a connection to a PCoIP server. The UDP port value sets the base UDP port to try. The UDP port range value determines how many additional ports should be tried if the base port attempt is not successful. The range spans from (base port) to (base port + port range).
This setting applies to the client only.
When Disabled or Not Configured, the base port is 50002 and the port range is 64. When Configured, the base port and port range values are applied as described above with a default base port of 50002 and a default port range of 64.
Configure PCoIP virtual channels
This policy enables virtual channels and controls which virtual channels operate over PCoIP sessions.
When the policy is enabled, for a virtual channel to be used in a PCoIP session it must be included on the virtual channel authorization list and not present on the virtual channel unauthorization list. A maximum of 16 virtual channels may be used.
Virtual channel authorizations:
When virtual channels are enabled, this value can be used to control which virtual channels are allowed. When this value is empty, all virtual channels are allowed. If the value is not empty then a virtual channel must be explicitly included in the authorization list to be allowed. To allow specific virtual channels, enter their names separated by the ‘|’ character. If the channel name contains the ‘|’ or ” characters, insert a ” before it. For example, enter the virtual channel named ‘awk|wardchannel’ as ‘awk|wardchannel’.
For example, the virtual channel authorization string to allow the mksvchan and vdp_rdpvcbridge virtual channels is ‘mksvchan|vdp_rdpvcbridge’.
Virtual channel unauthorizations:
When virtual channels are enabled, this value can be used to control which virtual channels are disallowed. When this variable is empty, no virtual channels are disallowed. To disallow specific virtual channels, enter their names separated by the ‘|’ character. If the channel name contains the ‘|’ or ” characters, insert a ” before it. As an example, to enter the virtual channel named ‘awk|wardchannel’ use the string ‘awk|wardchannel’.
As a usage example, the virtual channel unauthorization string to disallow the mksvchan and vdp_rdpvcbridge virtual channels is ‘mksvchan|vdp_rdpvcbridge’.
The Virtual Channel setting applies to both server and client. Virtual Channels must be enabled on both Server and Client for Virtual Channels to be used. For a particular virtual channel to be used, the virtual channel must be included on the authorization list and not included on the unauthorization list.
Since the most common use of virtual channels is to implement clipboard processing, there is a separate checkbox for clipboard processing which applies to the server only – the checkbox has no effect on a client. To disable remote clipboard processing, check the “Disable clipboard processing on PCoIP host” checkbox.
When the Virtual Channel configuration setting is Disabled or Not Configured, virtual channels are enabled and all virtual channels are allowed (including clipboard processing). When this setting is enabled, the individual settings are applied as described above with a default of virtual channels enabled, all virtual channels allowed including clipboard processing.
Configure PCoIP image quality levels
This policy enables control over how PCoIP renders images during periods of network congestion.
There are three settings which interoperate to allow fine control in network-bandwidth constrained environments: Minimum Image Quality, Maximum Initial Image Quality and Maximum Frame Rate.
The Minimum Image Quality setting allows a balance between image quality and frame rate for limited bandwidth scenarios. With limited bandwidth, there must be a trade-off between image quality and frame rate – this setting allows the ability to configure which is preferred.
The Minimum Image Quality value ranges between 30 and 100 with a default value of 50. A lower value allows a lower quality display (with potentially higher frame-rates) and a higher value allows higher image quality (with potentially lower frame rates) when network bandwidth is constrained. When network bandwidth is not constrained, the PCoIP protocol will maintain maximum quality regardless of the setting. The value of the setting must be set to a value which is less than or equal to the Maximum Initial Image Quality setting.
The Maximum Initial Image Quality setting can reduce the network bandwidth peaks required by the PCoIP protocol by limiting the initial quality of the changed regions of the display image. In a limited bandwidth scenario, this allows the configuration of which is preferred: a lower initial quality with more frequent updates or a higher image quality with less frequent updates.The Maximum Initial Image Quality value ranges between 30 and 100 with a default value of 90. A lower value will reduce the image quality of content changes and decrease peak bandwidth requirements. A higher setting will increase the image quality of content changes and increase peak bandwidth requirements. Note that the unchanged regions of the image will progressively build to a lossless (perfect) quality regardless of setting. The value of the Maximum Initial Image Quality must be set to a value which is greater than or equal to the Minimum Image Quality. The recommended Maximum Initial Image Quality setting value is 90 or lower to best utilize the available network bandwidth.
The Maximum Frame Rate setting is a mechanism to manage the average bandwidth consumed per user by limiting the number of screen updates per second. A higher Maximum Frame Rate setting may use more bandwidth but will provide less jitter (for smoother transitions in changing images such as video); a lower setting will use less bandwidth but will result in more jitter.
The Maximum Frame Rate value ranges between 1 and 120 frames per second and has a default value of 30 frames per second.
These three Image Quality settings apply to the soft host only and have no effect on a soft client.
When this policy is Disabled or Not Configured, the settings use the defaults given above. When this policy is Configured, the setting values are applied as described above using the default values as given above.
Enable Right SHIFT behavior when a PCoIP client is connected
This policy can be used to enable substitution of the Right SHIFT key with a Left SHIFT key, which allows the Right SHIFT key to function properly when using RDP through PCoIP. This may be useful when using RDP within a PCoIP session.
This policy applies to the server only and has no effect when set on a client.
When this policy is set to Disabled or not Configured, the substitution will not be performed. When this policy is Configured/Enabled, the substitution will be performed.
Enable the FIPS 140-2 approved mode of operation
When this policy is configured as Enabled, only FIPS 140-2 approved cryptographic algorithms and protocols are used to establish a remote PCoIP connection. Setting this policy to Enabled overrides any disabling of AES128-GCM encryption.
This policy applies to both server and client. Either endpoint or both may be configured to operate in FIPS mode. If a single endpoint is configured to operate in FIPS mode, this will limit the encryption algorithms which are available for session negotiation.
FIPS mode is available for View 4.5 and subsequent versions; for versions of View prior to View 4.5 (i.e. View 4.0, 4.0.1 and 4.0.2) FIPS mode is not available and configuring this policy will have no effect.
When this policy is set to Disabled or not Configured, FIPS mode is not used. When this policy is Configured/Enabled, FIPS mode is used.
Disallow console input behavior when a PCoIP client is connected
This setting can be used to disallow console input from the host whenever there is a client attached through PCoIP. This will ensure that a malicious user will not be able to provide input to the host locally when there is an active PCoIP remote session.
This policy applies to the server only and has no effect on a client.
When this policy is set to Disabled or Not Configured, console input will be allowed. When this policy is Configured/Enabled, console input will be disallowed.
Turn on PCoIP user default input language synchronization
This policy controls whether the default input language for the user in the PCoIP session is synchronized with the default input language of the PCoIP client endpoint.
This policy applies to the server only and has no effect on a client.
When this policy is Disabled or Not Configured, synchronization is disallowed. When this policy is Configured/Enabled the synchronization is allowed.
Use alternate key for sending Secure Attention Sequence
This setting can be used to specify an alternate instead of the Insert key for sending a Secure Attention Sequence (SAS). This setting can be used to preserve the Ctrl-Alt-Insert key sequence in guest operating systems that are launched from inside a PCoIP desktop. For example, a user can launch a vSphere Client from inside a PCoIP desktop and open a console on a virtual machine in vCenter Server. If the Ctrl-Alt-Insert sequence is used inside the guest operating system on the vCenter Server virtual machine, a Ctrl-Alt-Del SAS is sent to the virtual machine. This setting will enable Ctrl-Alt-<Alternate Key> to send a Ctrl-Alt-Del SAS to the PCoIP desktop.
This setting applies to the server only and has no effect on a client.
When this policy is set to Disabled or Not Configured, Ctrl-Alt-Ins will be used as the SAS. When this policy is set to Configured/Enabled, a drop-down menu must be used to specify the alternate key desired – the setting value cannot be left unspecified.
Disable sending CAD when users press Ctrl+Alt+Del
When this policy is enabled, users must press Ctrl+Alt+Insert instead of Ctrl+Alt+Del to send a Secure Attention Sequence (SAS) to the desktop during a PCoIP session. This setting might be enabled if users are confused when they press Ctrl+Alt+Del to lock the client endpoint and an SAS is sent to both the host and the guest.
This setting applies to the server only and has no effect on a client.
When this policy is not configured or is disabled, users can press Ctrl+Alt+Del or Ctrl+Alt+Insert to send an SAS to the desktop.