Testing the available bandwidth between machines with Iperf
If we ever need a tool to measure bandwidths or to check an optimal configuration of our network or between delegations, we can use the Iperf utility that through a client-server connection can show us information of great interest!
Official Website: http://sourceforge.net/projects/iperf/
And if we need a Windows version (compiled with Cygwin) we can download it from AKI.
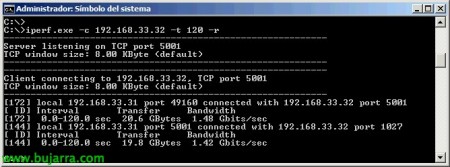
With 'iperf.exe -s’ It will start in server mode waiting for a client connection,
With 'iperf.exe -c DIRECCIÓN_IP -t120 -r’ We will be able to connect this client computer to the one running the iperf in server mode during 2 minutes of connection and monitor both outgoing and incoming traffic.
With the -f option we will change the output format to: Bit(b), bytes(B), Kilobits(k), Kilobytes(K), Megabits(m), Megabytes(M), Gigabit(g) or gigabytes(G).
With the -d option, you will generate bidirectional traffic simultaneously.
With -w we will send the TCP size (between 2 and 65,535 bytes).
With -p we will change the port, Default 5001.
With -i we will modify the interval so that it shows us the report.
With -u the tests will be with UDP.
With -b we will limit to a bandwidth.
With -m we will obtain the Maximum Segment Size (MSS), which is the largest amount of data that a computer/device supports in a single segment, Unfragmented. MSS = MTU – TCP header and IP header. TCP header and IP header = 40 bytes. Examples of MTU: Ethernet LAN:1500 bytes, PPPoE: 1492 bytes (ADSL), Ring Token or 16Mb/sec: 17914 bytes and dial-up: 576 bytes
For more information we will run the -h option
Usage: Iperf [-s|-C host] [options]
Iperf [-h|–help] [-v|–version]
Client/Server:
| -f -i -l -m -p -u -w -B -C -M -N -V |
–format –interval –len –print_mss –port –UDP –window –bind –compatibility –mss –nodelay –IPv6Version |
[kmKM] # #[KM] # #[KM] # |
format to report: Kbits, Mbits, KBytes, MBytes seconds between periodic bandwidth reports length of buffer to read or write (default 8 KB) print TCP maximum segment size (MTU – TCP/IP header) server port to listen on/connect to use UDP rather than TCP TCP window size (socket buffer size) bind to “host”, an interface or multicast address for use with older versions does not sent extra msgs set TCP maximum segment size (MTU – 40 bytes) set TCP no delay, disabling Nagle’s Algorithm Set the domain to IPv6 |
Server specific:
| -s -Or -D |
–Server –single_udp –daemon |
run in server mode run in single threaded UDP mode run the server as a daemon |
Client specific:
| -b -c -d -n -r -t -F -I -L -P -T |
–bandwidth –client –dualtest –num –tradeoff –Time –fileinput –Stink –listenport –parallel –ttl |
#[KM] “host” #[KM] # # |
for UDP, bandwidth to send at in bits/sec (default 1 Mbit/sec, implies -u) run in client mode, connecting to “host” Do a bidirectional test simultaneously number of bytes to transmit (instead of -t) Do a bidirectional test individually time in seconds to transmit for (default 10 secs) input the data to be transmitted from a file input the data to be transmitted from stdin port to recieve bidirectional tests back on number of parallel client threads to run time-to-live, for multicast (default 1) |
Miscellaneous:
| -h -v |
–help –version |
print this message and quit print version information and quit |