Create or join a domain on Windows 2008 + RODC or Read Only Domain Controller,
Create a domain in Windows 2008 – HERE
Join a Windows domain 2008 – HERE
Installing a read-only domain controller – Read Only Domain Controller – RODC – HERE
Join a domain using Microsoft Windows 2008 Core (RODC) – HERE
First a description for those who do not know what a domain is: A domain is a grouping of computers around centralized servers that store the list of users, access level for each, and other information related to user accounts, Team accounts, groups, Printers… what we will call objects. Everything can be managed from a centralized location thanks to policies/policies.
These servers are Domain Controllers (Windows 2000, 2003 or 2008) and centralize the group's security management, Of course, each domain controller has different roles, some will be more important than others, even though Microsoft says that there is no domain controller more important than another.
Of course, each domain can have subdomains in turn, The most comfortable way to manage another part of the company, divide it into large departments or groups of companies and not delegate permissions to other users who do not have access to domains other than their own.
Create a domain in Windows 2008,
In this part of the document we will see how to create a domain or subdomain in Windows 2008, The normal way.

First, We open the “Server Manager” or “Server administration” from the “Administrative Tools”,

Click on “Add Roles” or “Add features”,
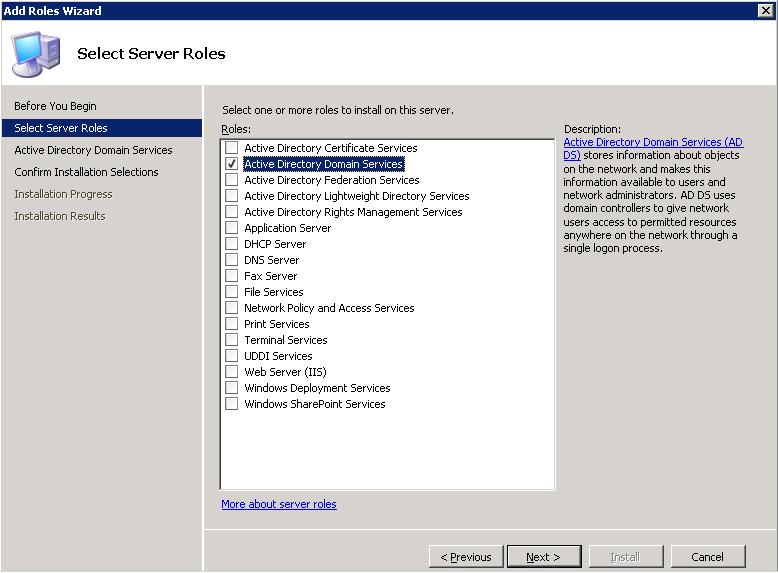
Mark “Active Directory Domain Services” and “Next”,

He tells us what AD DS does (Active Directory Active Services), that stores information about users, computers and other devices on the network. “Next”,
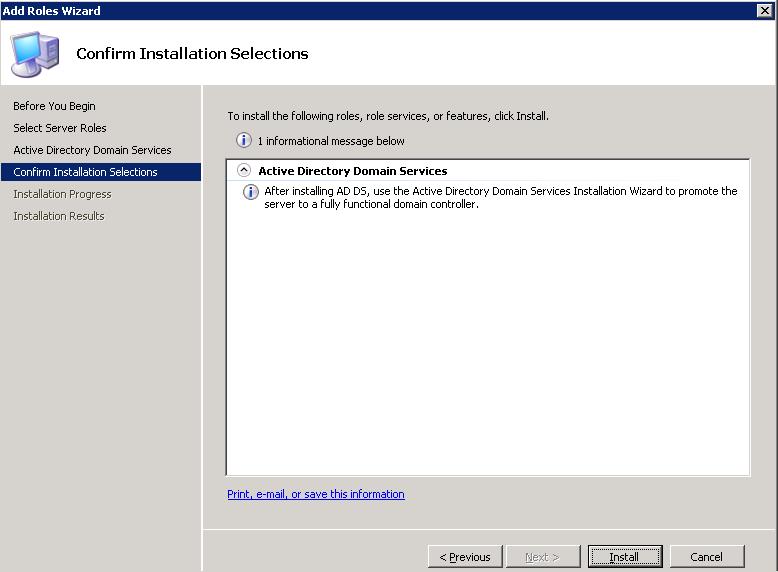
We confirm that what we are going to install are the domain services and click on “Install”
… installing ADDS…

Ok, it already shows us that the role is installed, Close.
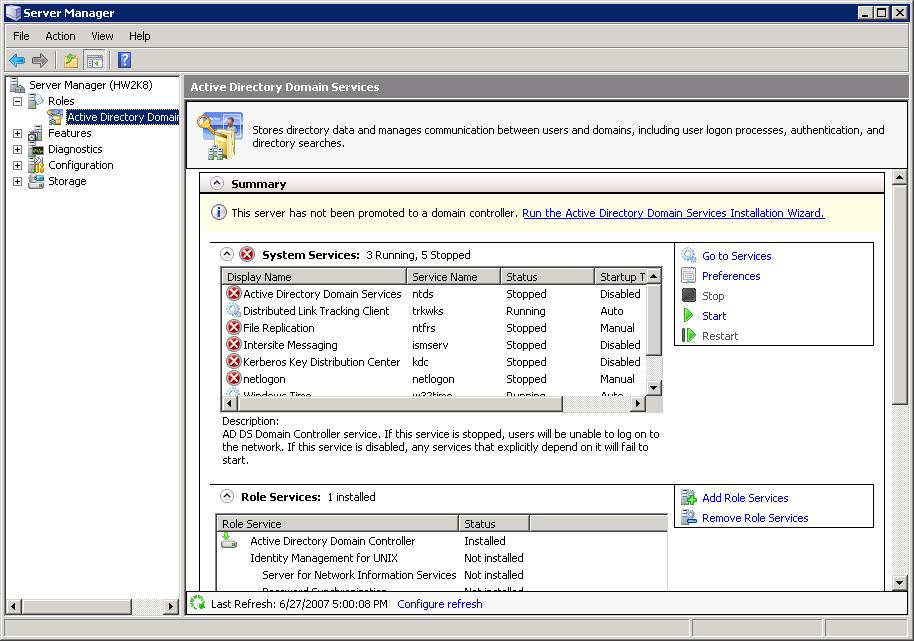
Now what you have to do is promote it as a domain controller, from the “Server Manager” or “Server administration” Click on “Roles” > “Active Directory Domain Services” and in the “Run the Active Directory Domain Services Installation Wizard” or “Run the Active Directory Services Installation Wizard”.

We can perform advanced installation, But we're not interested, Click on “Following”,
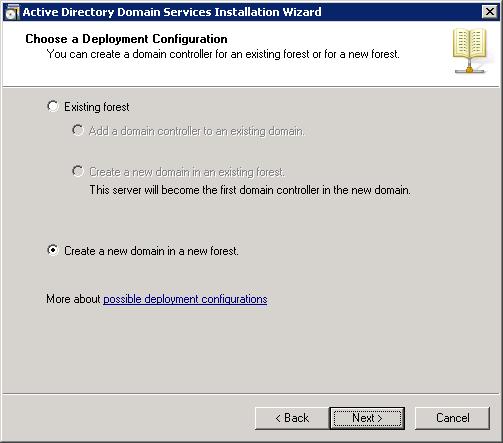
If we are going to join a domain tree, we would click on the first option, And then we would see if what we are going to do is this as another domain controller for an existing domain or create a new domain in an existing forest. But what matters, if it is the first domain for the first forest we click on the second option: “Create a new domain in a new forest” & “Following”,

We indicate the domain name we are going to create, Has to carry a point “.”. Normally, It is usually the same as the public domain of the Internet, But it doesn't have to be the same, Microsoft usually advises that if you don't know which one to put, put a .local. Whatever, “Next”,

Checks that this domain does not exist on the same network…

This would be the NetBIOS name of the domain, Continue,

This is where we have to indicate the functional level of the forest, since we are creating a new forest. Ideally, you should set the level of the forest as high as possible for safety, but this will allow us various possibilities having PC's or servers with old versions.
The functional forest level “Windows Server Codename Longhorn” Introduces a New Level of Function for Forests and Domains. Although the Windows Server forest level “Longhorn” (that will be released under a different name) does not provide any new features, ensures that all domains in the forest are at the Windows Server functional level “Longhorn”, allowing for two improvements. The first, The most current replication engine in the distributed file system (DFS) for the SYSVOL share, offering greater stability, Security and Performance. The second, AES encryption support 256 bits with the Kerberos authentication protocol. Although the latest functional level provides the best performance, you will be able to continue using the lower tiers when migrating to Windows Server “Longhorn”.
Several schema extensions have also been introduced to support new features, all compatible with the schemes currently in use. Domain controllers running on Windows Server “Longhorn” will be able to coexist and work in combination with those running on Windows Server 2003.

Being the first domain controller, we must mark that it has to be a DNS server for name resolution, so you have to have the DNS Server check checked, although you can also put the DNS service on another server, But it doesn't make sense. It will also be a global catalog to manage user logins. And this server, being the first in the domain, cannot be RODC (Read-Only Domain Controller – Read Only Domain Controller), but if we put in an additional one it could be. “Following”,

Logically because it is the first DNS server, Continue, “Following”,

We indicate the directories to store the Active Directory database; where it will store the log files, The LOG; and what will be the SYSVOL directory to store the files to be replicated between the domain controllers (Scripts, Policies…), “Following”,

We indicate the administrator's password in case we need to boot the Domain Controller in Directory Services restore mode from F8 when rebooting. “Following”,

We can save the features listed here for use with another domain controller so that it is an unattended installation file, An archive of responses. The only thing that wouldn't work for us is that we're creating a domain, This makes sense to use when we join a domain as an additional domain controller. “Following” to start creating the ADDS,

… We wait for it to be set up…
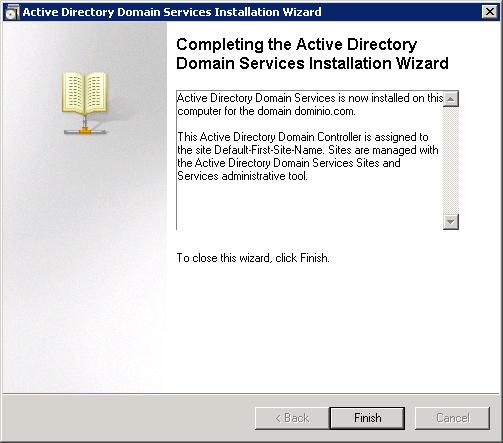
Ok, “Finish”, The domain is already created and we already have our first domain controller.

You have to restart for the changes to take effect.
In this part of the document we will simply see the options that must be made when we want to join a server to an existing domain, as an additional domain controller.
Installing a read-only domain controller – Read Only Domain Controller – RODC,
One of the new features that Microsoft Windows brings 2008 Server or Longhorn is that we can have a domain controller on the read-only network, This makes sense for security, in case we need to have a domain controller in a delegation and we don't want anyone to touch anything.
RODC addresses some issues that are common to a branch office (BO). It may happen that BOs do not have a local Domain Controller, or that they have it, but do not comply with the necessary security conditions that this entails, plus the necessary bandwidth, or the technical staff's own experience and/or knowledge.
As a result of the problems mentioned above, RODC provides the following features:
Read-only AD DS Database.
Unidirectional replication.
Credential Caching.
Administrator role separation.
Read-only DNS.
Read-only AD DS Database
Except passwords, an RODC contains all the objects and attributes that a typical DC has. However, Of course, changes that impact the base of an RODC cannot be made. Any kind of changes that you want to make, must be carried out in a non-RODC DC, and then impacted via replication at the RODC base.
Applications that require read-mode access to the AD base will have this without any problem. However, those that require write access, receive an LDAP referral, which will point directly to a non-RODC DC.
Unidirectional replication
The one-way replication of RODC, which applies to both AD DS and DFS, allows, in case any changes can be made with the intent to modify the integrity of the AD database, is not replicated to the rest of the DCs. From an administrative point of view, This type of replication reduces the overhead of Bridgehead Servers, and monitoring of such replication.
Credential Caching
Default, RODC does not store user or computer credentials, except, of course,, the account corresponding to the RODC itself and the special krbtgt account that each RODC has. Storage of any other type of credential must be explicitly enabled.
It should be noted that limiting Credential Caching to only those users who authenticate to the RODC, it also limits the security of these accounts. However, Only these accounts will be vulnerable to possible attacks.
Disabling Credential Caching leads to any authentication requests being redirected to a non-RODC DC. It's possible, however, modify the Password Replication Policy to allow user credentials to be cached on an RODC.
Administrator Role Separation
It is possible to delegate administrative permissions only for one RODC, limiting the performance of administrative tasks only in the RODC, and not in other DCs.
Read-only DNS
The DNS service on an RODC does not support direct client updates. As a consequence of this, nor does it record NS records of any integrated zone containing. When a customer tries to update their DNS record against the RODC, The server returns a referral, That of course, is subsequently used by the customer to update their registration. However, the RODC also requests replication of the specific registry.

To install an RODC, What you need to do is check during the Domain Controller Promotion “Read-only domain controller (RODC)”.
Join a domain using Microsoft Windows 2008 Core (RODC),
In this part of the document we will simply see the options that must be made when we want to join a server to an existing domain, as an additional domain controller but using Windows Core, Eyeball, This domain controller will only be read-only, will be a Read Only Domain Controller.

To join as an additional domain controller in an existing domain as a read-only controller (RODC) which is the function that a Core can implement, The following command must be executed: dcpromo /unattend /InstallDns:yes /confirmGC:yes /replicaOrNewDomain:replica /ReplicaDomainDNSname:”DOMAIN” /databasePath:”C:Windowsntds” /logPath:”C:Windowsntdslogs” /sysvolpath:”C:Windowssysvol” /safeModeAdminPassword:XXXXX /rebootOnCompletion:Yes
Logically, These are the most generic parameters, We can save these parameters in an unattended installation file, Usually called unattend.txt to be able to use it directly with the rest of the servers: dcpromo /unattend:unattend.txt
On this Microsoft website there are all the possible parameters to use with the unattended installation file: HTTP://technet2.microsoft.com/windowsserver2008/en/library/d660e761-9ee7-4382-822a-06fc2365a1d21033.mspx
www.bujarra.com – Héctor Herrero – Nh*****@*****ra.com – v 1.0