Enabling ABE – Access-based Enumeration on Windows 2008
Microsoft Windows 2008 it already comes by default with a utility called Access based Enumeration that allows you to hide directories to which users do not have NTFS permissions, instead of seeing them as usual, it hides them directly, avoiding user confusion.
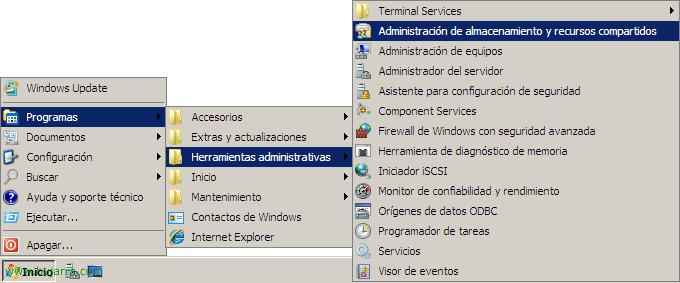
To set this up, We have to go to the “Administrative Tools” and open “Storage and share management”,
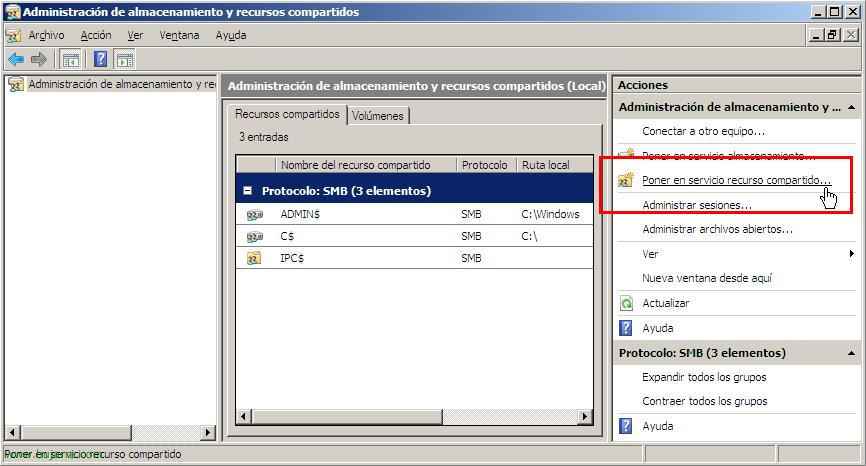
Click on the menu of “Actions” in “Serve Share…”
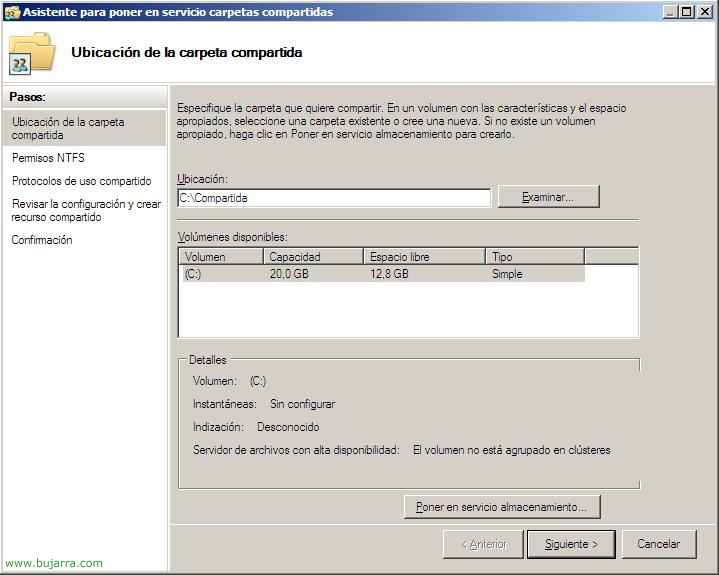
We look for the folder we want to share, For example, I created a C one: Shared Call. Click on “Following”,
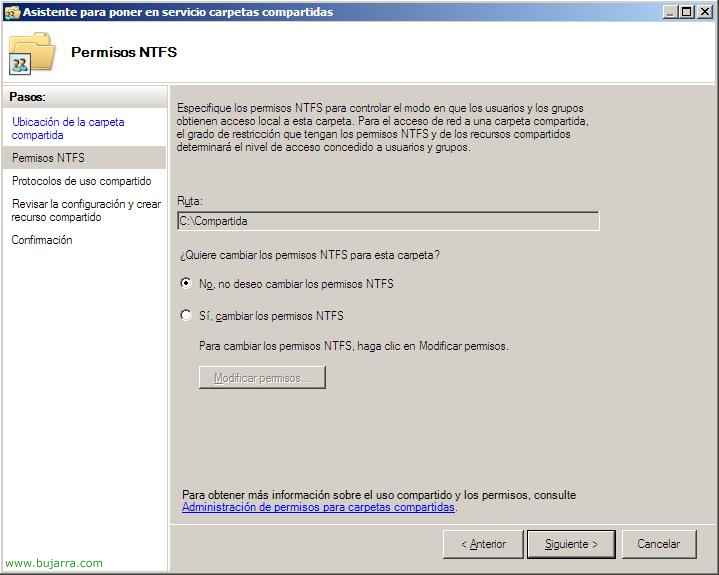
If we want, we can configure the NTFS permissions from here by clicking on the second option, but in this case I will not do it since it is not a question of explaining this issue, We, “Following”,
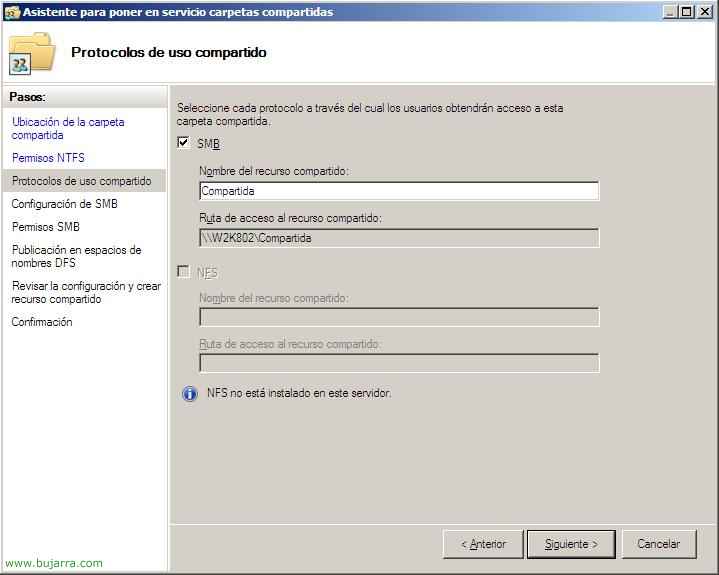
Check the SMB check, which is the protocol that Windows will use 2008 Default for network shares, we will deal with NFS in another document, “Following”,
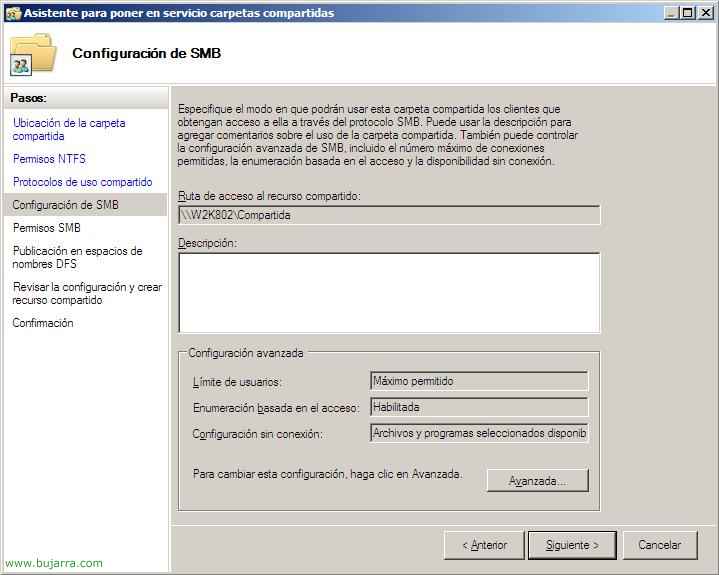
We see what would be the form of access to this network resource, and from the “Outpost…” We could change different options, including EBA access-based enumeration (Access-based Enumeration – ABE). “Following”,
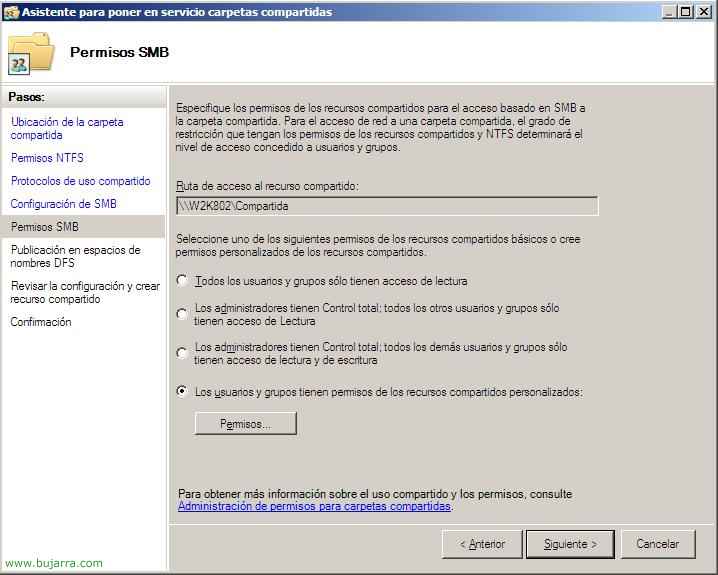
We can configure permissions here at the share level, we mark the one that interests us, “Following”,
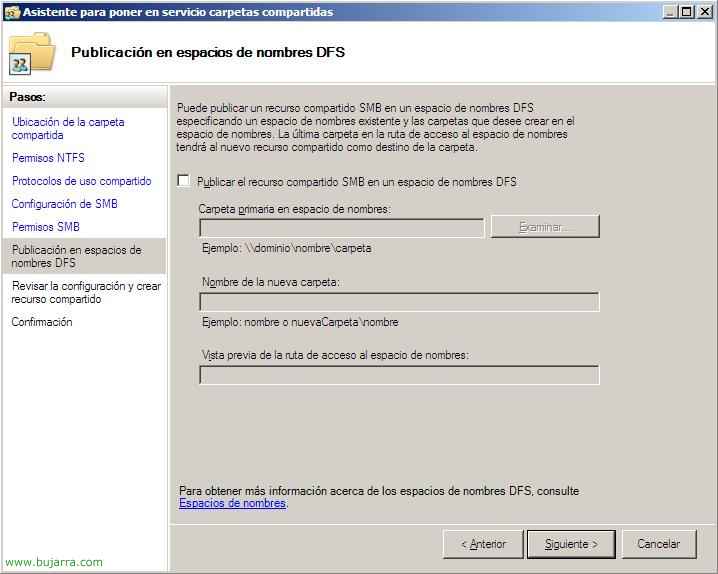
If we use DFS we can enable it from here and publish it to any DFS namespace we have, Neither is this case, “Following”,
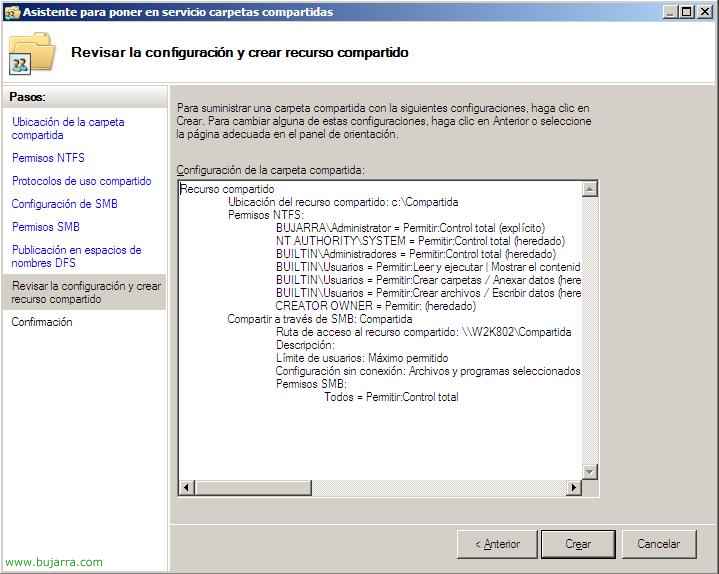
This would be the summary to create this share, If we agree, click on “Create”,
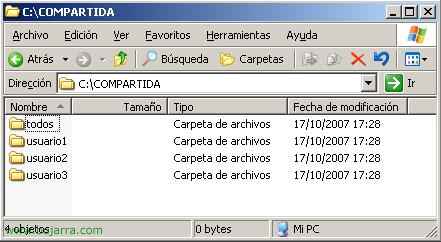
This would be the example of a folder that we have shared by entering locally as an administrator on the server, It is an example to see which directories it has. Of course, NTFS permissions are configured in each directory, which can only be entered by the user in each directory.
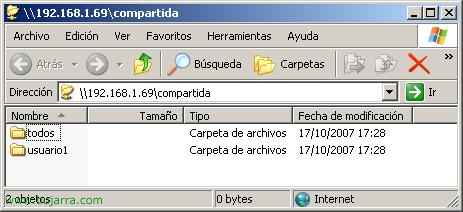
If we log in with a user who has access only to the directory “user1” and “all” Here's what you'll see online,
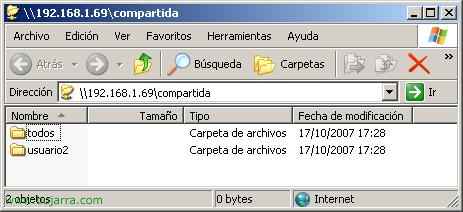
And logically if we log in with a user who only has access to the directory “user2” and “all” Here's what you'll see. It's a way to prevent users from seeing directories that they don't have access to.