Replication between two HP EVAs 4400 with Continuous Access
Continuous Access, is native replication of HP StorageWorks Enterprise Virtual Array Family arrays (EVE). We will look at the necessary configuration at both the SAN Switch level and the Command View level (CV) To perform synchronous or asynchronous replication (depending on the locations for example).
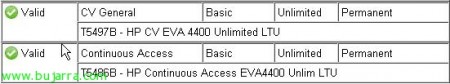
I cannot begin without first mentioning that in order to carry out this type of replication it is necessary to have specific licensing (according to your EVA specifications…), I mean, if we have a CV license for 4Tb and want to replicate them, we will need to purchase a 4Tb Continuous Access license.
In my case: (unlimited license on both CV and CA 🙂 )
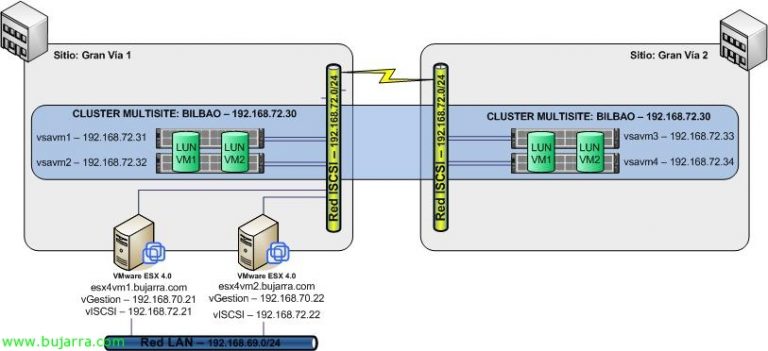
That being said, I present the environment to be configured: two data centers in the same building (To, B) with two fiber switches in each (11 and 12, 21 and 22). In each DPC, two HP EVA's 4400 with a single set of discs (12HD 300Gb Fiber); In addition, a server that will act as Command View in each DPC (CV_A and CV_B) And to finish, a virtualization infrastructure divided between the two data centers (4 ESX in CPD A and 2 ESX in CPD B, with a single vCenter on the CV_A server. All fibers go double way except for the two servers' CV’ who have a single HBA.
With the infrastructure presented, the first thing we must do is correctly configure the zoning of the fiber switches so that the two CVs are able to see the cockpit of the opposite DPC. This is a requirement to perform replication; so at the end, we will have two CVs from which we can manage our two EVAs.
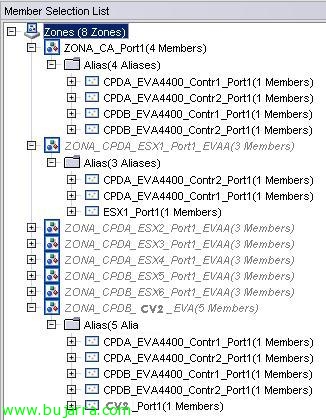
On the Switch 11 (the first of the CPD A), I have the following zones set up:
- ZONA_CA_Port1: It is the area that contains the ports 1 of both EVA controllers.
- ZONA_CPDA_ESX'x'_Port1_EVAA: It is the area that contains the first ESX1 HBA with access to the ports 1 of both controllers of the VPA of the DPC A.
- ZONA_CPDB_CV2_EVA: It is the area where I give permits to the CV2 to the ports 1 of both EVA controllers.
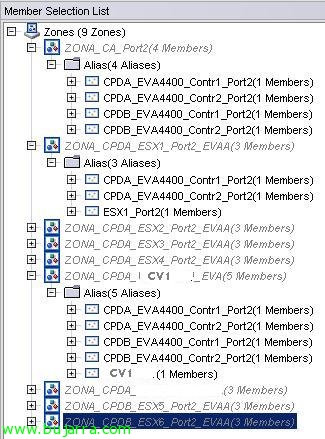
On the Switch 12 (the second of CPD A), I have the following zones set up: (This switch is the one that has the CV1 connected)
- ZONA_CA_Port2: It is the area that contains the ports 2 of both EVA controllers.
- ZONA_CPDA_ESX'x'_Port2_EVAA: It is the area that contains the second HBA of the ESX'x’ with access to ports 2 of both controllers of the VPA of the DPC A.
- ZONA_CPDB_CV1_EVA: It is the area where I give permits to the CV1 to the ports 2 of both EVA controllers.
On the Switch 21 (the first of the CPD B), I have the following zones set up: (This switch is the one that has the CV2 connected)
- ZONA_CA_Port1: It is the area that contains the ports 2 of both EVA controllers.
- ZONA_CPDA_ESX'x'_Port1_EVAA: It is the area that contains the first HBA of the ESX'x’ with access to ports 1 of both controllers of the VPA of the DPC A.
- ZONA_CPDB_CV2_EVA: It is the area where I give permits to the CV2 to the ports 2 of both EVA controllers.
On the Switch 22 (the second of CPD B), I have the following zones set up:
- ZONA_CA_Port2: It is the area that contains the ports 2 of both EVA controllers.
- ZONA_CPDA_ESX'x'_Port2_EVAA: It is the area that contains the first HBA of the ESX'x’ with access to ports 2 of both controllers of the VPA of the DPC A.
- ZONA_CPDB_CV1_EVA: It is the area where I give permits to the CV1 to the ports 2 of both EVA controllers.
It should be mentioned, than the ideal, is to allow ESX zones access to the EVA ports of the DPC B, so if we had to move the infrastructure to work against the EVA of the CPD B, We'd have half the work done.
With the above zoning settings, we get the CVs of both DPCs to be able to administer the two EVAs as shown in the image.
The first thing we will have to configure to start replicating, is a DR Group or Data Replication Group. In these, we must group those LUNs of the same type; in my case, I have multiple LUNs that serve as DataStores in VMware so I'll create a single DRGroup for those LUNs.
To do this,, We will click on “Data Replication” and “Create Data Replication Group”.
In the first half, We have the name of the DRG, the origin que toma por defecto es la EVA desde donde estas creando el grupo de replicación. The destiny, marcaremos la EVA a la que queremos replicar… como en mi caso solo tengo dos, no tengo posibilidad a fallo… The Source Vdisk, es la LUN que deseamos replicar. (cada LUN solo puede estar en un DRGroup)
En la segunda parte, digamos que tenemos las opciones “avanzadas”:
- Write mode: Mode de escritura, sincrono o asincrono:
- Synchronous. This mode provides the best data protection. In synchronous write mode, the array acknowledges I/O completion after the data is cached on the source and destination arrays. This process maintains identical data on a source DR group and its destination DR group at all times.
- Asynchronous. This mode provides the best host I/O performance. In asynchronous write mode, the source array acknowledges host writes before the data is replicated on the destination array. This process allows faster host I/O than synchronous mode. From a data protection standpoint, there can be brief instances in which the data is not identical in the source and destination DR group. Asynchronous write mode can be basic or enhanced, depending on the controller software version.
- Destination Disk Group: Grupo de discos de destino. In my case, como solo tengo una bandeja de discos por EVA, solamente tengo un Disk Group.
- Destination redundancy: Podemos modificar el nivel de RAID del destino o dejar como en el origen…
- Destination host access: podemos establecer el nivel de acceso que tendra la LUN…
- Log Size: Tamaño de LOG. ¡¡OJO!! El tamaño de log por defecto a partir del firm 9.0.0 es de 102,40GB. The logs are saved with a RAID1 redundancy and in both cabins so keep an eye out for the space you have available… I have set it to 10240Mb… which seems more than enough to me.
- Source Log Disk Group: The disk group where the logs are stored on the source. This could be useful if we have two groups of discs with different coenxions.. FIBRA vs. FATA for example.
- Destination Log Disk Group: The disk group where the logs are stored on the source.
- Failsafe on unavail member: Failsafe data protection is a feature which blocks host I/O to all of the virtual disks in a DR group when components fail or become unavailable. This feature protects data by maintaining write ordering in the source and destination DR groups. (There is no better explanation)…
- Suspend on links down: Suspend the replica if any link is in the Down state.
- Suspend on full copy: If 'enable’ Remote replication is suspended when a 'full copy' is launched.
- Comments: No comments…
Once the options have been chosen, above we will click on “Create” and the first 'full copy' will begin. Be careful when launching it as it can impact system performance…
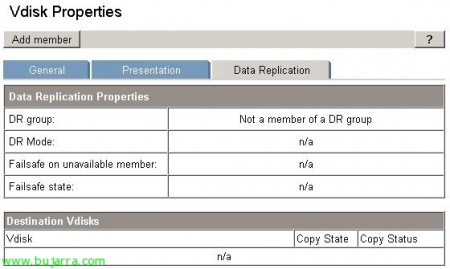
Once the first replica is created and finished, If we have selected the synchronous writing mode it will be in continuous change “Destination”. Nevertheless, selecting the DRGroup in question and navigating through the tabs that appear in the image, we can change all the options that are given at the time of its creation. In addition to viewing the status of the replica…
If we wanted to add a LUN to an already created DRGroup, we will have to do it from the properties of the LUN on the DataReplication tab, Add member.
- DR Group: It allows us to indicate some of the DRGs already created
- Destination disk group: The target disk group
- Destination redundancy level: The RAID level at the destination.
We could also from here, jump to create a new DRG, With the button “Create DR group”…
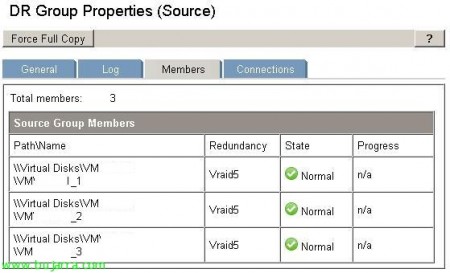
Here's how the Members tab of a DRGroup is displayed with 3 LUNs replicating.